Table of contents
- Pedagogy in education
- Why is it called pedagogy?
- Types of Pedagogy Education
- Features of pedagogy?
- Innovative Ideas to Practice Pedagogy in Education.
- Why is pedagogy important?
- What is the difference between pedagogy and teaching?
- Popular Pedagogy Approaches for Teachers
- Various Perspectives of Pedagogy
The field of education is undergoing rapid advancements, with continuous improvements enhancing the education ecosystem. As educators or learners, it is essential to cope with the new changes and understand the concept of pedagogy in education. An organized pedagogy has the potential to accelerate institutional growth.
In this blog post you are going to explore the significance of pedagogy and its impact on education and learning.
Now let’s commence from here.
Pedagogy in Education:
Pedagogy in education refers to the theory and practice of teaching and instruction. It focuses on the methods, approaches, and strategies teachers use to facilitate learning and promote students’ educational development. It continues to be a central concept in pedagogy in education.
Do you know why it is termed as pedagogy, not some xyz?
No worries, here is the answer.
Why is it Called Pedagogy?
Pedagogy is called such because it reflects the historical focus on the role of teachers in guiding and instructing students. It emphasizes the importance of the teacher’s knowledge, skills, and instructional practices in creating effective learning experiences. Pedagogy emphasizes the teacher’s role in structuring and facilitating learning, designing curriculum, assessing student progress, and promoting educational outcomes.
Pedagogy in education has some exciting features that benefit teachers, schools and students.
Let’s look into each feature in detail.
Features of Pedagogy:
Pedagogy in education encompasses various features that contribute to effective teaching and learning. Some key features of pedagogy include:
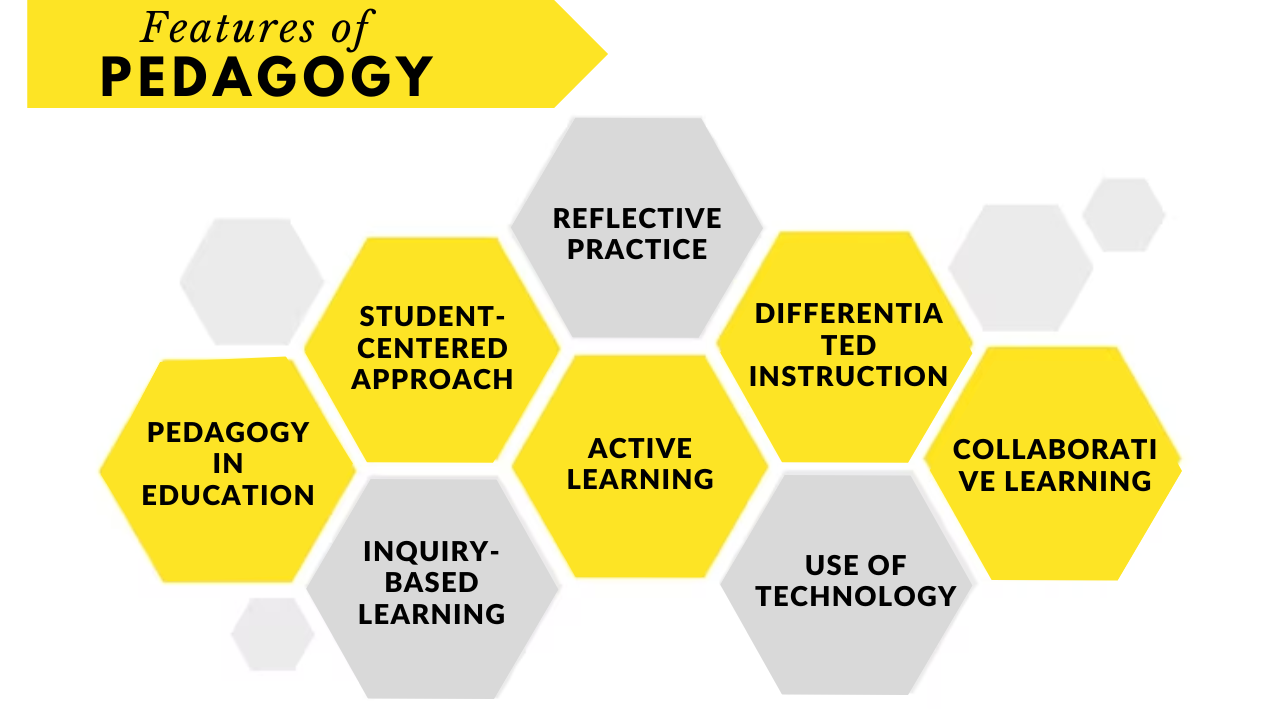
Student-Centered Approach: Pedagogy emphasizes placing the student at the center of the learning process. It focuses on understanding students’ needs, interests, and learning styles, tailoring instruction to meet their requirements
Active Learning: Pedagogy promotes active learning, encouraging students to engage in hands-on activities, discussions, problem solving skill, and critical thinking. It moves away from passive information transfer and encourages students to construct knowledge actively.
Differentiated Instruction: Pedagogy in education recognizes the diversity of learners and supports differentiated instruction. It involves adapting teaching methods, resources, and assessments to accommodate students’ varying abilities, interests, and learning styles.
Collaborative Learning: Pedagogy in education fosters collaborative learning environments where students work together in groups, discussing ideas, sharing perspectives, and solving problems collectively. It encourages peer interaction, cooperation, and the development of social skills.
Inquiry-Based Learning: Pedagogy in education promotes inquiry-based learning, where students explore questions, investigate problems, and develop a deep understanding through self-directed exploration. It nurtures curiosity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills.
Assessment for Learning: Pedagogy in education recognizes the importance of ongoing assessment to inform instruction. It includes formative assessments that provide timely feedback to students, allowing them to reflect on their progress and improve.
Reflective Practice: Pedagogy in education encourages teachers to engage in reflective practice, continually evaluating their teaching methods, assessing student outcomes, and adjusting instruction based on feedback and reflection.
Use of Technology: Pedagogy in education incorporates technology as an instructional tool to enhance learning experiences, facilitate access to information, and promote digital literacy skills.
Cultural Sensitivity and Inclusivity: Pedagogy in education values cultural sensitivity and inclusivity, acknowledging and respecting diverse backgrounds, perspectives, and experiences. It promotes an inclusive learning environment where every student feels valued and supported.
Lifelong Learning: Pedagogy in education instills a love for learning and equips students with skills, attitudes, and habits that promote lifelong learning. It prepares them to adapt to new challenges, embrace growth, and pursue continuous personal and professional development.
Are you aware of the innovative ideas to practice pedagogy in education? If not please go through the below mentioned innovative ideas to practice pedagogy in education.
Innovative Ideas to Practice Pedagogy in Education

Project-Based Learning: Design projects that require students to explore real-world problems, conduct research, collaborate, and present their findings. This approach promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and application of knowledge.
Flipped Classroom: Flip the traditional classroom model by providing instructional materials, such as videos or readings, for students to review outside class. Classroom time can then be used for discussions, activities, and hands-on learning.
Gamification: Incorporate elements of games, such as challenges, rewards, and leaderboards, into the learning process. Gamification motivates students, fosters engagement, and makes learning enjoyable.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Use VR and AR technologies to create immersive learning experiences. Students can explore virtual environments, conduct experiments, and visualize complex concepts.
Collaborative Learning Spaces: Create flexible learning spaces that promote collaboration, communication, and creativity. Arrange furniture and resources for group work, discussions, and project-based activities.
Mindfulness and Well-being: Integrate mindfulness practices, relaxation techniques, and well-being activities into the curriculum. These practices support students’ social-emotional development and create a positive learning environment.
Authentic Assessments: Move beyond traditional exams and incorporate authentic assessments that mirror real-life scenarios. Use portfolios, presentations, projects, and performances to assess students’ knowledge and skills.
Blended Learning: Combine face-to-face instruction with online learning platforms and resources. This approach allows for personalized learning, flexibility, and access to various learning materials.
Why is Pedagogy Important?
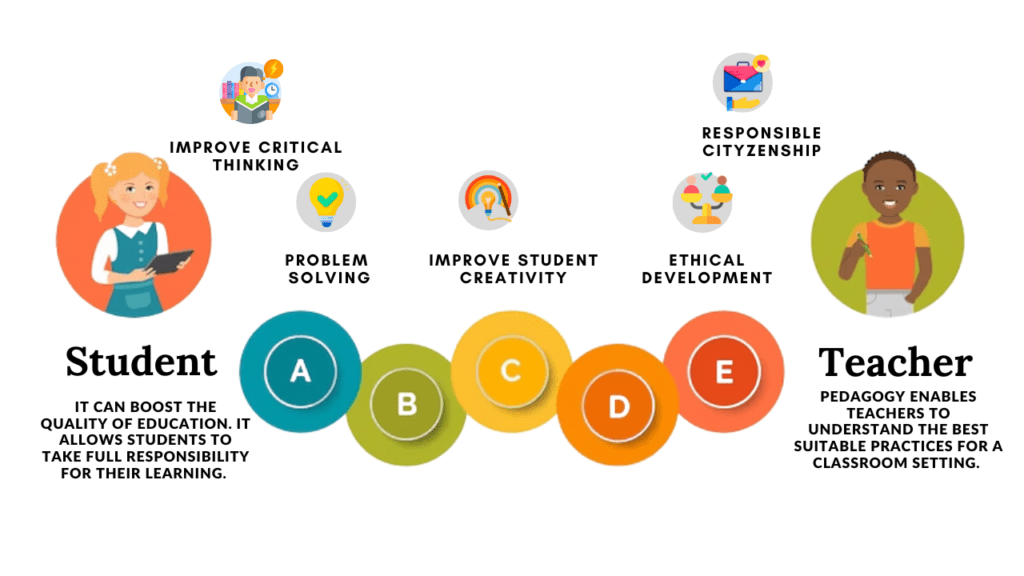
Pedagogy is important for several reasons:
- Pedagogy provides teachers with strategies and approaches to facilitate effective learning.
- It actively engages students in the learning process, and pedagogy enhances their motivation, interest, and participation in the classroom.
- It focuses on developing higher-order thinking skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and analytical reasoning.
- Pedagogy recognizes the diverse needs, abilities, and learning styles of students.
- It addresses their social, emotional, and ethical development, fostering values, empathy, and responsible citizenship.
- Promotes the creation of active learning environments where students actively participate, collaborate, and communicate.
- It helps teachers refine their instructional practices, incorporate new research-based strategies, and stay updated with emerging trends and advancements in Pedagogy in education.
- Effective pedagogy in educational outcomes, including academic achievement, higher retention rates, and increased student satisfaction.
Difference Between Pedagogy and Teaching:
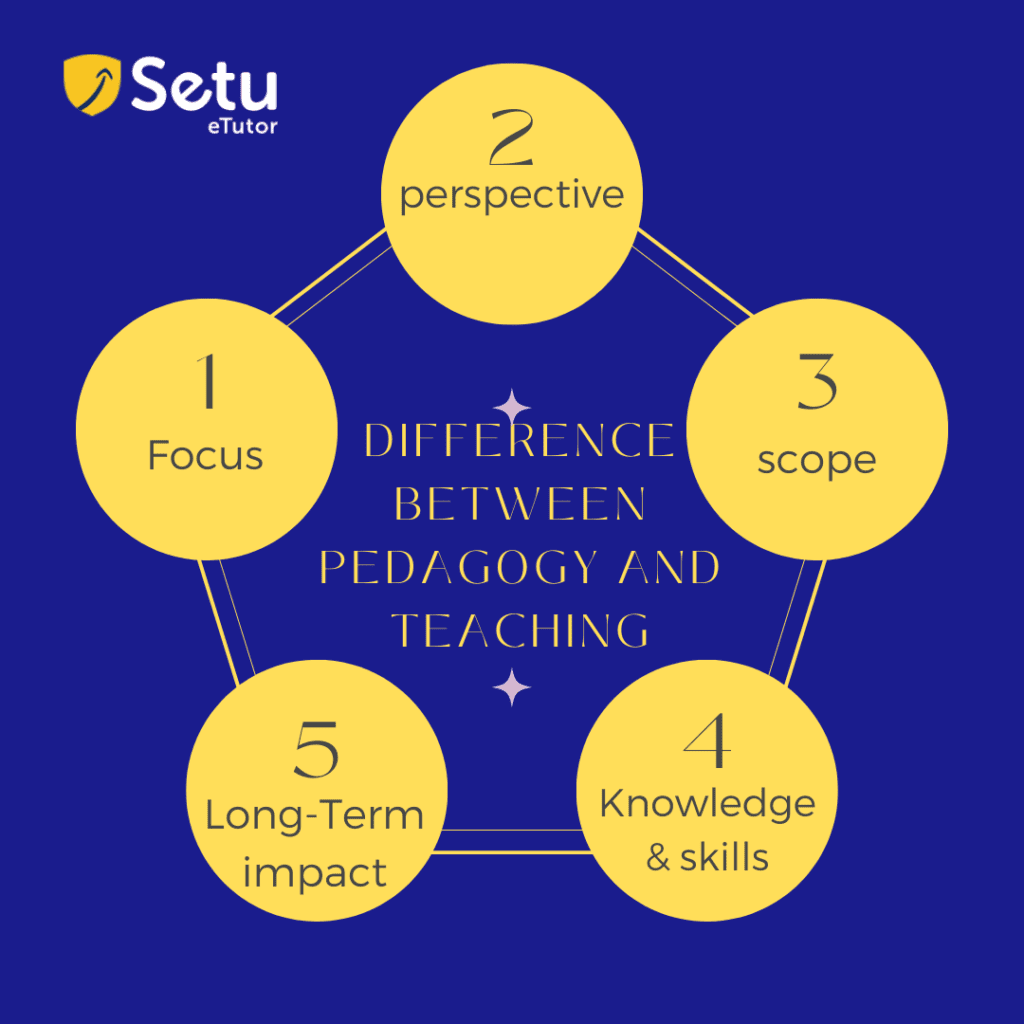
Pedagogy and teaching are related concepts but have distinct differences.
Focus: Pedagogy refers to the broader framework and principles of education, including the theories, methods, and strategies used to facilitate learning. It encompasses the entire Pedagogy in education process, from curriculum development to instructional design and assessment. On the other hand, teaching specifically refers to imparting knowledge, skills, and information to students.
Perspective: Pedagogy takes a learner-centered approach, considering the needs, interests, and developmental stages of students. It focuses on understanding how students learn best and designing instruction accordingly. On the other hand, teaching is more instructor-centered, focusing on delivering information and guiding students through the learning process.
Scope: Pedagogy encompasses a broader range of educational contexts and approaches, including formal and informal education, different age groups, and various subject areas. It includes theories and practices from educational psychology, curriculum development, assessment, and instructional design. Teaching is more specific to the classroom context and the direct interaction between the teacher and students.
Knowledge and Skills: Pedagogy involves a deep understanding of educational theories, learning theories, instructional methods, assessment strategies, and curriculum development. It requires knowledge of effective teaching practices, educational psychology, and research-based approaches. Teaching involves practically applying pedagogical knowledge and skills to engage students, deliver content, facilitate learning activities, and assess student progress.
Long-term Impact: Pedagogy focuses on developing students’ critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and lifelong learning habits. It aims to foster holistic development, self-directed learning, and the acquisition of transferable skills. Teaching, while important for delivering content and guiding students, is more immediate and focused on the immediate learning objectives and outcomes.
Popular Pedagogy Approaches for Teachers:
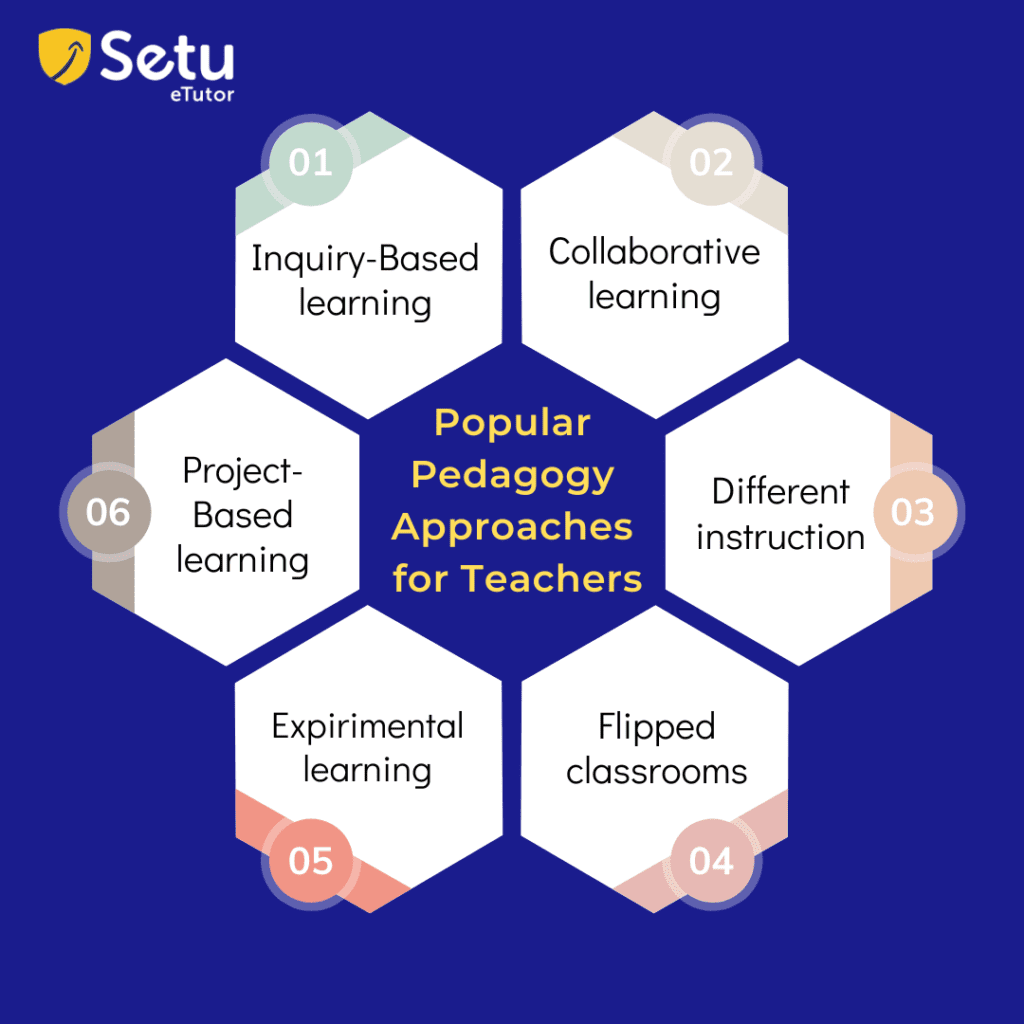
Teachers can utilize several popular pedagogy approaches to enhance their instructional practices and promote effective learning. Here are a few examples:
Inquiry-Based Learning: This approach involves posing open-ended questions or problems to students, encouraging them to explore, investigate, and seek answers on their own. It promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and curiosity. SETU is a knowledge-based platform where students can post questions and get answers from the teachers through student connect.
Collaborative learning: This approach encourages students to work together in groups or teams, fostering peer interaction, collaboration, and the exchange of ideas. It promotes communication skills, teamwork, and a sense of collective learning.
Differentiated Instruction: This approach involves tailoring instruction to meet students’ diverse needs, learning styles, and abilities. It involves adjusting content, teaching methods, and assessment strategies to accommodate individual differences.
Flipped Classroom: This approach involves students reviewing instructional content, such as videos or readings, outside of class and using class time for interactive discussions, hands-on activities, and deeper understanding. It allows for more student-centered and active learning experiences.
Experiential Learning: This approach emphasizes learning through direct experience and reflection. It involves hands-on activities, field trips, simulations, and real-life applications to engage students and enhance understanding.
Project-Based Learning: In this approach, students engage in in-depth projects or investigations that require them to apply knowledge and skills to real-world situations. It promotes problem-solving, research skills, creativity, and presentation abilities.
Conclusion:
Pedagogy is the backbone of education and learning. It guides educators in designing and implementing effective instructional practices that inspire and empower students. Our AI-based platform SETU in sync with NEP 2020, leverages pedagogical principles to attain transformative educational experiences, effectively bridging the learning gaps.
This content provides you with the most valuable information you require. If you find anything not specifically mentioned, please drop your queries in the comments section or contact us here. We would consider your suggestions.










Leave a reply