What is NCERT
NCERT stands for National Council of Educational Research and Training, established in 1961 by the government of India. National Council of Educational Research and Training plays a significant part in influencing the educational landscape of India. The key objective of this autonomous body is to bring together all the students through education.
The following seven existing government organizations were combined to form the NCERT.
They are:
- Central Institute of Education
- Central Bureau of Textbook Research
- Central Bureau of Educational and Vocational Guidance
- Directorate of Extension Programmes for Secondary Education
- National Institute of Basic Education
- National Fundamental Education Centre
- National Institute of Audio-Visual Education
What is NCERT Used for?
In India, National Council of Educational Research and Training is largely utilized for educational reasons. Here are a few notable applications of NCERT:
Textbooks: National Council of Educational Research and Training creates and publishes textbooks based on the NEP standards for various disciplines and grade levels. Numerous state education boards and schools connected to the CBSE frequently use these texts. They offer students a standardized and thorough curriculum that includes a variety of topics like math, physics, social sciences, languages, and more.
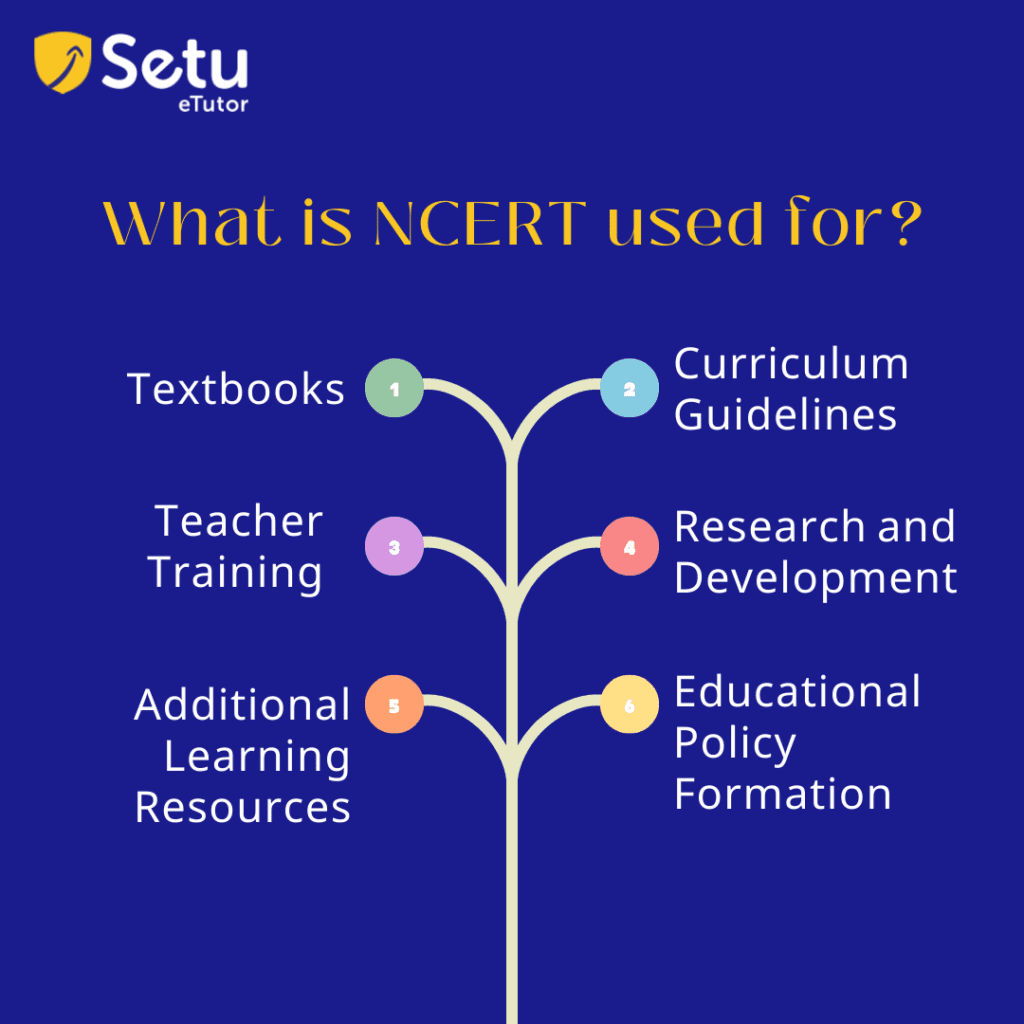
Curriculum Guidelines: National Council of Educational Research and Training establishes curricular framework and recommendations for many topics and grade levels. These recommendations support educational boards and institutions in developing curricula and syllabi, guaranteeing a nationwide consistent and well-organized educational system.
Teacher Training: To improve teachers’ pedagogical abilities, subject-matter expertise, and instructional strategies, National Council of Educational Research and Training offers training courses and seminars. These initiatives aid in raising the standard of instruction and learning in classrooms.
Research and Development: NCERT carries out research projects in pedagogy, curriculum development, and education. The output of these studies are applied to enhance educational policies, instructional strategies, and student learning outcomes in educational institutions.
Additional Learning Resources: National Council of Educational Research and Training creates additional learning resources such as manuals, example tests, question banks, and instructional websites. These tools assist teachers and students, promoting greater comprehension and test preparation.
Educational Policy Formation: At the national level, National Council of Educational Research and Training is a crucial advisor and contributor to the creation of educational policy. The group offers the Ministry of Education and other educational entities professional advice on various educational topics.
NCERT Online Study Material:
Through its official website, NCERT offers students access to online study materials. The following are some salient aspects of the National Council of Educational Research and Training’s online study guides:
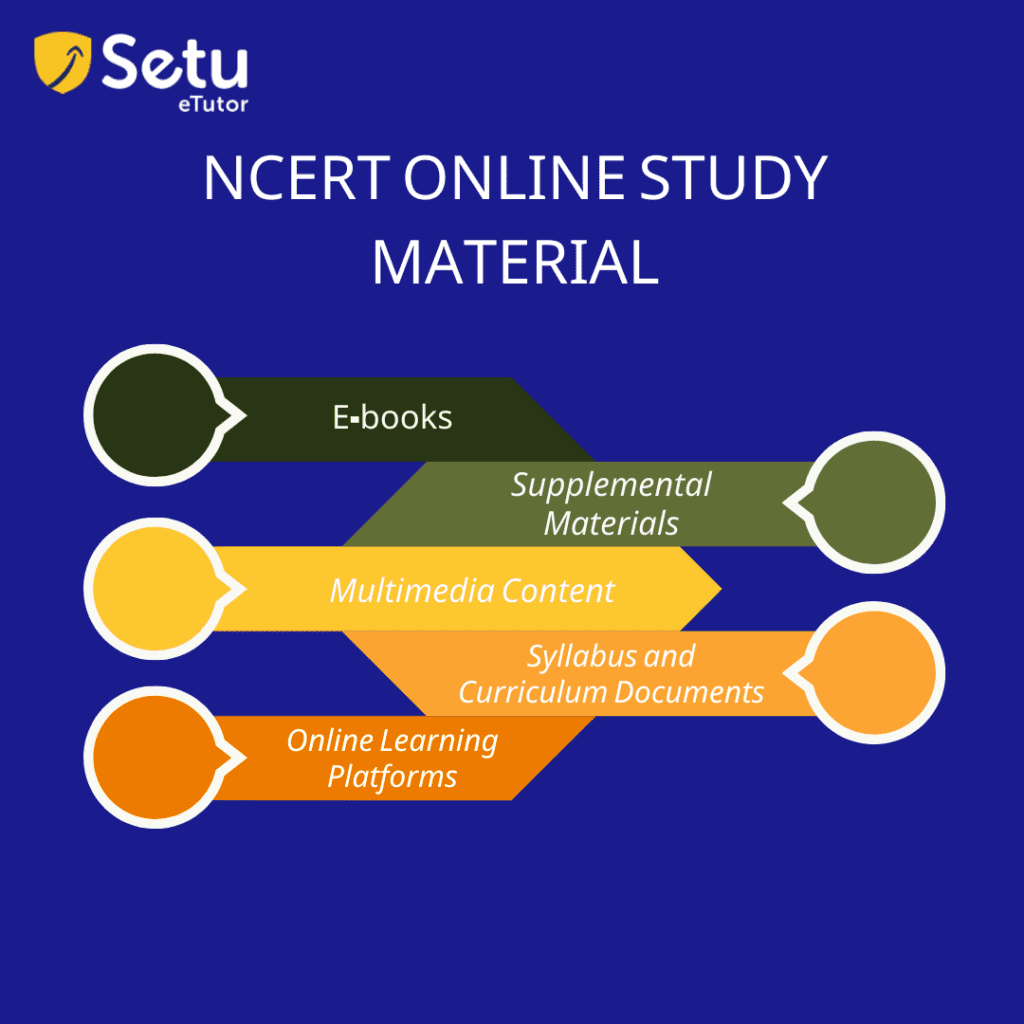
E-books: NCERT provides free access to and downloads of the electronic versions of its textbooks. These e-books are offered for various disciplines and grade levels, from elementary to upper secondary. The textbooks are available for online reading or download for offline use by students.
Supplemental Materials: In addition to textbooks, NCERT offers supplemental materials like sample papers, practice sets, model problems, and model test questions. These tools aid students in better conceptual understanding and exam preparation.
Multimedia Content: Online learning materials from NCERT incorporate multimedia elements, including audio, video, and interactive modules. These materials offer a fun and dynamic learning environment that improves students’ conceptual knowledge and memory.
Syllabus and Curriculum Documents: The official syllabus and curriculum documents for various disciplines and classes are available on the NCERT website. Students can use these materials to comprehend the subjects and NCERT-mandated learning objectives.
Online Learning Platforms: NCERT has also created several online learning portals, including e-Pathshala and DIKSHA (Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing). These platforms offer a variety of interactive e-books, videos, quizzes, and other digital learning activities.
You can visit the official National Council of Educational Research and Training website (www.ncert.nic.in) or look into online resources like DIKSHA and e-Pathshala to get the NCERT’s study materials.
Difference Between NCERT and CBSE:
Even though they are closely associated, National Council of Educational Research and Training and CBSE are two distinct entities in the Indian educational system. The following are the main differences between NCERT and CBSE:
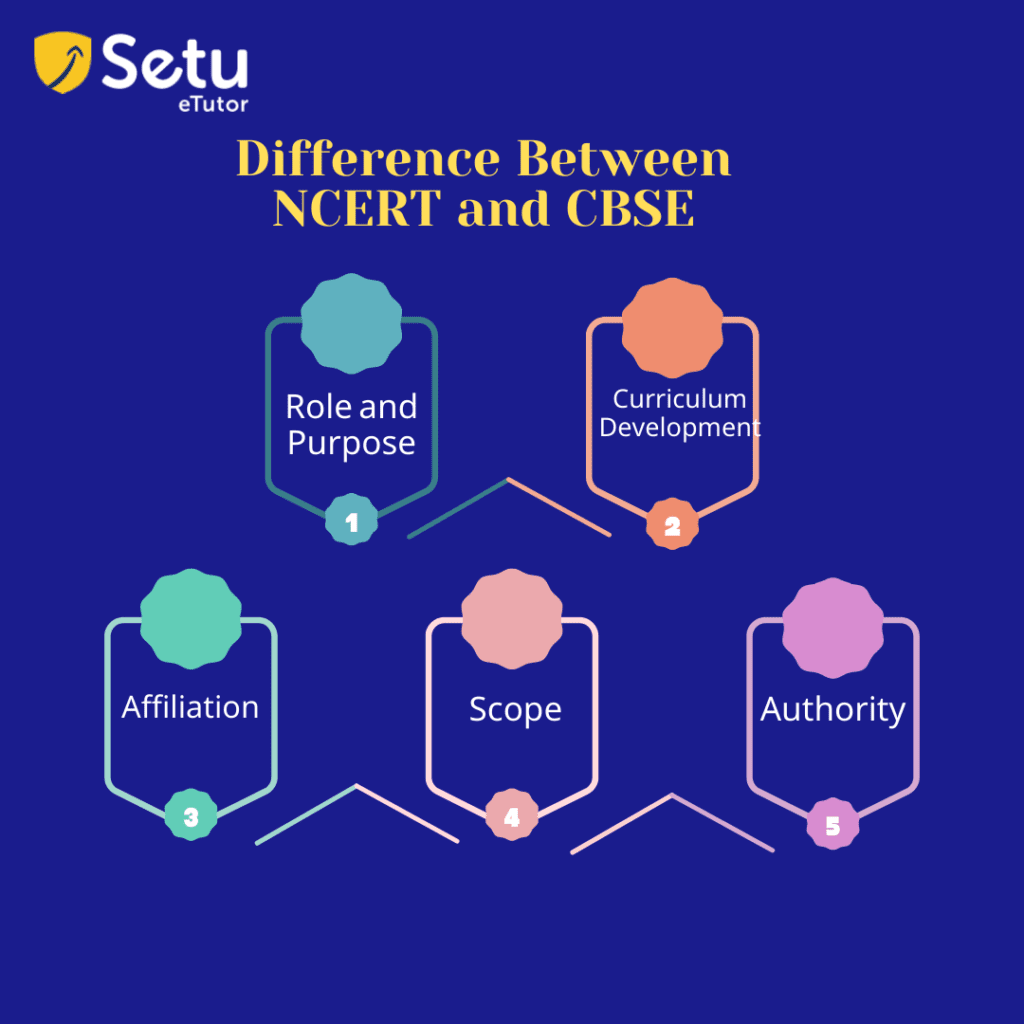
Role and Purpose:
NCERT: The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an independent agency tasked with creating and disseminating educational resources, carrying out research, and offering programs for teacher training. NCERT focuses on developing curricula, writing textbooks, establishing educational regulations, and conducting research.
CBSE: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), a national educational body, oversees and controls the academic standards, exams, and curricula of the institutions with which it is connected. Board exams are administered by CBSE, which also establishes standards for educational institutions.
Curriculum Development:
NCERT: National Council of Educational Research and Training creates and designs the curriculum structure and guidelines across various disciplines and grade levels. Based on these standards, it produces uniform textbooks and educational materials that schools from various education boards use.
CBSE: CBSE accepts the NCERT-developed curriculum but can add new subjects and make amendments as needed. The CBSE ensures that the schools connected with it follow the established curriculum and rules.
Affiliation:
NCERT: National Council of Educational Research and Training doesn’t have a direct stake in a school’s affiliation. It focuses on creating instructional resources and content for schools across all boards.
CBSE: CBSE is in charge of officially recognizing and affiliating schools. Schools that want to become affiliated with CBSE must meet specific requirements, follow CBSE regulations, and teach the CBSE-recommended curriculum.
Scope:
NCERT: CBSE-affiliated schools are not the only ones that can use National Council of Educational Research and Training’s resources and materials. Schools connected to numerous state education bodies also frequently employ them.
CBSE: The primary purpose of the CBSE educational board is to oversee and manage examinations for the schools that are a part of it. It establishes its own set of guidelines for the institutions with which it is affiliated.
Authority:
NCERT: National Council of Educational Research and Training is an independent organization that works in designated fields and is housed within the Ministry of Education (formerly known as the Ministry of Human Resource Development).
CBSE: The Ministry of Education’s autonomous CBSE organization has the power to control and manage the schools that are a part of it.
NCERT- Functions and Guidelines:
NCERT Functions:
The key functions of National Council of Educational Research and Training are:
- Curriculum development
- Textbook development
- Teacher training
- Educational Policy Formulation:
- Research and development
National Council of Educational Research and Training Guidelines:
NCERT provides guidelines for the following. They are:
- Curriculum Guidelines: National Council of Educational Research and Training sets the curriculum guidelines and framework for different subjects and grade levels. These guidelines guide schools and educational boards to design their curriculum and syllabus, ensuring a standardized and structured education system.
- Textbook Guidelines: National Council of Educational Research and Training provides guidelines for the development of textbooks. These guidelines ensure that the textbooks align with the curriculum, promote conceptual understanding, and cater to the diverse learning needs of students.
- Pedagogical Guidelines: National Council of Educational Research and Training offers pedagogical guidelines and best practices for teachers to enhance their teaching methodologies. These guidelines focus on student-centred approaches, activity-based learning, and technology integration in education.
- Examination Guidelines: National Council of Educational Research and Training provides guidelines for conducting examinations, including the format, marking scheme, and evaluation procedures. These guidelines aim to ensure fair and consistent assessment practices across schools.
- Inclusive education guidelines: NCERT promotes inclusive education and provides guidelines for creating inclusive classrooms and learning environments. These guidelines emphasize the importance of catering to the diverse needs of students, including those with disabilities or special educational needs.
- Continuous Professional Development Guidelines: NCERT offers guidelines for the continuous professional development of teachers. These guidelines encourage teachers to engage in ongoing learning, reflective practices, and collaborative professional development activities.
Conclusion:
National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), is essential to the growth and development of the nation’s educational system.
National Council of Educational Research and Training conducts research projects, initiatives, and surveys to find areas where education can be improved. The outcomes of these initiatives guide the creation of teaching-learning resources, curriculum adjustments, and policy decisions.
NCERT seeks to advance quality education, guarantee a standardized curriculum, enhance teaching methods, and meet the various learning needs of students through its functions and guiding principles. Its efforts help in improving and developing India’s educational system.










Leave a reply