Table of contents
Introduction
What are summative assessments?
What is the difference between formative assessments and summative assessments?
What are the types of summative assessments
What are the challenges faced by summative assessments in the classroom?
Benefits of summative assessments
How can teachers create a Summative Assessment that Measures Student Achievement?
Conclusion
Introduction:
By delving into the essence and purpose of summative assessment, we can shed light on its vital role in education as a crucial link between teaching and learning.
Assessment encompasses a range of evaluation techniques, including tests, quizzes, exams, and assignments, all geared toward measuring student learning outcomes.
In this regard, we developed a platform SETU incorporating all the assessment techniques that benefit students and teachers. Educators gain valuable data on students’ progress, identifying areas of improvement and areas that may require further attention. Simultaneously, students can determine their learning gaps and receive feedback that guides them toward their next steps in the learning process.
This post explores the types and benefits of comprehensive assessment, emphasizing its significance in facilitating learning and providing valuable insights for educators.
What are Summative Assessments?
Summative assessments are evaluations conducted at the end of a learning period to assess a student’s overall understanding and knowledge of a subject or course. These assessments are typically used to determine a student’s final grade or to evaluate the effectiveness of a specific instructional approach or curriculum.
However, they are just one part of a comprehensive assessment approach, including formative assessments, quizzes, homework assignments, and other methods supporting ongoing learning and development.
What is the Difference Between Formative and Summative Assessments?
The critical distinction between formative and summative assessments lies in their time frame and nature.
Summative assessments:
- Comprehensive assessments are typically one-time tests or assignments at the end of a specific learning period.
- They require clear expectations and a set timeline to ensure student fairness and consistency.
- Since they hold higher stakes, teachers must carefully plan and communicate the expectations and assessment schedule to give students the best chance to succeed.
Summative Assessment Examples:
Examples of summative assessment include:
- Final exams
- End-of-semester exams
- Final Project
- Paper
Formative assessments:
- Formative assessments are ongoing and can occur as frequently as necessary to support student learning.
- Formative assessments are designed to be more informal and interactive, allowing students to engage in the learning process actively.
- These assessments help teachers gauge students’ progress and understanding, providing valuable feedback to guide instructional adjustments in real time.
Formative assessment examples:
- Pre-class open-ended questions
- Live multiple-choice poll
- Draw a map understanding of the given topic.
- Write one to two sentences of the lecture delivered in the class.
To know more, please, check out how our formative assessments contribute to student growth and learning.
Next, we will delve into the types of Comprehensive Assessments.
What are the Types of Summative Assessments?
Various types of summative tests are used in education to evaluate students’ overall understanding and knowledge at the end of a learning period. Here are some common types of summative assessments:
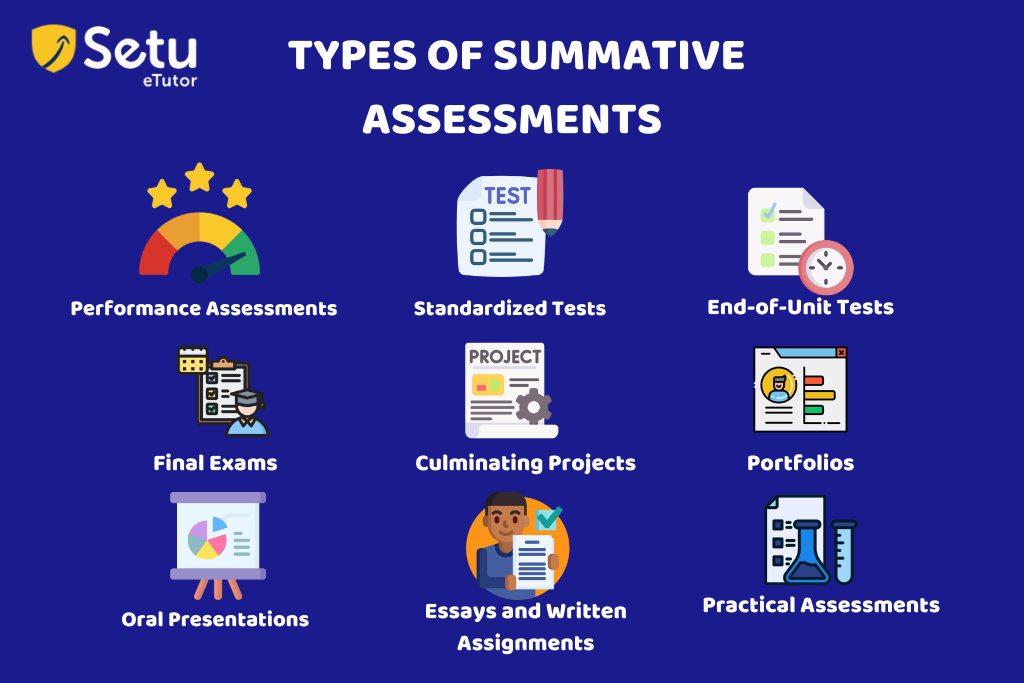
- Final Exams: These comprehensive assessments cover the content and concepts taught throughout the course. They are usually given at the end of a semester or academic year.
- Standardized Tests: These assessments are designed to measure a student’s knowledge and skills against a standardized set of criteria.
- End-of-Unit Tests: These assessments are given after a specific unit of study, testing students’ grasp of the material covered in that unit.
- Culminating Projects: Some courses may require students to complete a significant project or research assignment that showcases their understanding and application of the subject matter.
- Portfolios: Students compile their work samples, projects, and assignments, demonstrating their progress and achievements in different areas.
- Performance Assessments: These assessments require students to demonstrate their skills and knowledge through practical tasks or simulations, such as presentations, debates, or laboratory experiments.
- Oral Presentations: Students may be evaluated on their ability to communicate and present information effectively.
- Essays and Written Assignments: Students are assessed based on their written responses to questions or prompts, demonstrating their understanding of the subject matter.
- Practical Assessments: Common in subjects like music, arts, or physical education, these assessments evaluate students’ abilities in hands-on activities or performances.
What are the Challenges Faced by Summative Assessments in the Classroom?
Summative assessments in the classroom can face several challenges that impact their effectiveness and fairness. Some of the common challenges include:
- Limited Assessment Scope
- High-Stakes Pressure
- Limited Time for Assessment
- One-Time Evaluation
- Inadequate Feedback
- Standardization Challenges
- Cultural and Linguistic Bias
- Limited Representation of Skills
- Disruptions and Test Anxiety
- Overemphasis on Grades
What are the Benefits of Summative Assessments?
While summative tests have numerous benefits, it is essential to use them in conjunction with formative assessments, which offer ongoing feedback and support to enhance the learning process. Combining both assessment types ensures a well-rounded and practical approach to promoting student learning and achievement.
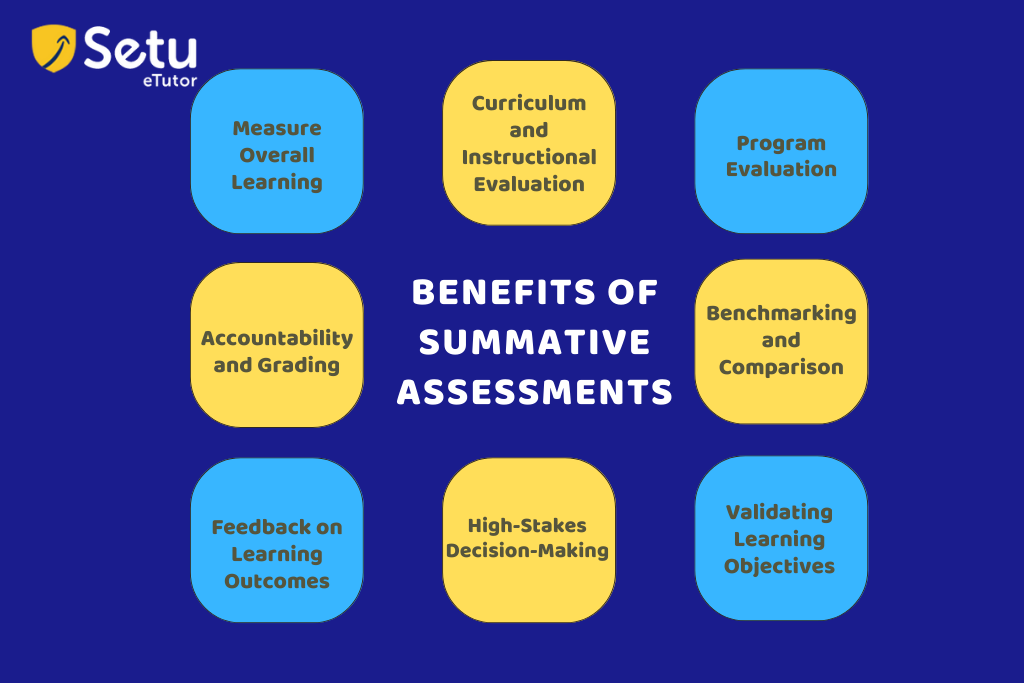
Here are some key benefits of using summative assessments:
- Measure Overall Learning: Summative assessments comprehensively evaluate students’ overall understanding and knowledge at the end of a learning period, offering a clear picture of what students have learned.
- Accountability and Grading: They help establish accountability by providing a standardized and objective method of grading students’ performance. It allows educators, students, parents, and institutions to assess progress and academic achievements.
- Feedback on Learning Outcomes: Summative assessments offer valuable feedback to students, indicating their strengths and areas that need improvement. This feedback helps students understand their progress and guides them in setting future learning goals.
- Curriculum and Instructional Evaluation: They help educators evaluate the effectiveness of their teaching strategies and the curriculum’s alignment with learning objectives. This data informs instructional decisions, allowing teachers to make necessary adjustments for better learning outcomes.
- Program Evaluation: Summative assessments can assess the overall effectiveness of educational programs, helping academic institutions identify areas of success and areas that may require improvement.
- High-Stakes Decision-Making: Summative assessments sometimes determine students’ promotion to the next grade level or eligibility for further academic opportunities, making them essential in high-stakes decision-making processes.
- Benchmarking and Comparison: Summative assessments, particularly standardized tests, provide a basis for comparing students’ performance across schools, districts, or national and international levels.
- Validating Learning Objectives: By aligning summative assessments with specific learning objectives, educators can ensure that the intended outcomes of the curriculum are achieved.
How can teachers create a Summative Assessment that Measures Student Achievement?
Creating a practical summative assessment requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are the steps to create a Summative Assessment that Measures Student Achievement. They are:
- Define clear learning objectives.
- Choose appropriate assessment formats (e.g., multiple-choice, essays).
- Align questions with learning objectives.
- Ensure fair and unbiased wording.
- Review and edit for clarity and accuracy.
- Establish a rubric for consistent grading.
- Pilot test the assessment with a sample group.
- Set a reasonable time limit for completion.
- Provide clear instructions to students.
- Administer the assessment under controlled conditions.
- Analyze results to evaluate student achievement.
- Use feedback to improve future assessments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, summative assessments are crucial in evaluating students’ overall understanding and mastery of course content. Summative assessments offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of instructional methods and curriculum by providing a snapshot of their achievement after learning has occurred.
Educators must use the data from comprehensive assessments to identify areas of improvement, guide instructional strategies, and support student learning effectively. Summative tests can be powerful tools for measuring student achievement and promoting continuous educational growth.
Please find out more exciting information on formative assessments in our blog. And explore how SETU helps in improving student learning outcomes. Schedule a demo today.








Leave a reply